Glossary of Terms Used in Photochemistry
[A] [B] [C]
[D] [E] [F]
[G] [H] [I]
[J] [K] [L]
[M]
[N] [O] [P]
[Q] [R] [S]
[T] [U] [V]
[W] [X] [Y]
[Z]
NON-ADIABATIC ELECTRON TRANSFER
See diabatic electron transfer
NORMAL REGION (for electron transfer)
In plots relating rate constants for electron
transfer, or quantities related to it, with the standard Gibbs
energy for the reaction (DGo),
the region for which the rate constants increase with increasing exergonicity
of the reaction is called the normal region. This region is predicted
by the Marcus theory for
outer-sphere electron transfer for the case of DGo
 l in the Marcus equation.
l in the Marcus equation.
n 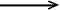 p* TRANSITION
p* TRANSITION
An electronic transition described approximately as promotion of an
electron from a "nonbonding" (lone-pair) n orbital
to an "antibonding" p orbital designated
as p*.
n-p* STATE
An excited state related to the ground
state by a n 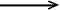 p* transition.
p* transition.
n 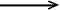 s* TRANSITION
s* TRANSITION
An electronic transition described approximately as promotion of an
electron from a "nonbonding" (lone-pair) n orbital
to an "antibonding" s orbital designated
as s*. Such transitions generally involve
high transition energies and appear close to or mixed with Rydberg
transitions.
NATURAL LIFETIME
Same as radiative lifetime.
The use of this term is discouraged.
NEODYMIUM LASER
A CW or pulsed laser emitting radiation from excited Nd+3
principally occurring around 1.06 mm (the
precise position depends on the matrix). The Nd+3 is present
as a dopant in suit-able crystals (e.g., yttrium-aluminium garnet,
YAG) or in suitable glasses (phosphate, silicate, etc.).
See solid state lasers.
NEUTRAL-DENSITY FILTER
See attenuance filter.
NITROGEN LASER
A source of pulsed semi-coherent superradiance
mainly around 337 nm. The lasing species is molecular nitrogen.
See gas lasers.
NON-ADIABATIC PHOTOREACTION
Same as diabatic photoreaction.
Use of double negative is discouraged.
Compare adiabatic photoreaction.
NON-LINEAR OPTICAL
EFFECT
An effect brought about by electromagnetic radiation the magnitude
of which is not proportional to the irradiance.
Non-linear optical effects of importance to photochemists are harmonic
frequency generation, lasers, Raman
shifting, upconversion, and others.
NON-RADIATIVE DECAY
Disappearance of an excited species due to a radiationless
transition.
NON-VERTICAL ENERGY TRANSFER
An energy transfer process which has a low Franck-Condon
factor.
See Franck-Condon principle.
NORRISH TYPE I PHOTOREACTION
a-Cleavage
of an excited carbonyl compound leading to an acyl-alkyl radical
pair (from an acyclic carbonyl compound) or an acyl-alkyl biradical
(from a cyclic carbonyl compound) as a primary
photoproduct; e.g.,
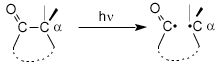
NORRISH TYPE II PHOTOREACTION
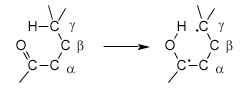
Intramolecular abstraction of a g-hydrogen
by an excited carbonyl compound to produce a 1,4-biradical
as a primary photoproduct;
e. g.,