Glossary of Terms Used in Photochemistry
[A] [B] [C]
[D] [E] [F]
[G] [H] [I]
[J] [K] [L]
[M]
[N] [O] [P]
[Q] [R] [S]
[T] [U] [V] [W]
[X] [Y] [Z]
CADMIUM-HELIUM LASER
See Helium-Cadmium laser.
CAVITY DUMPING
Periodic removal of coherent radiation from a laser cavity.
CHARGE HOPPING
Electron or hole transport between equivalent sites.
CHARGE RECOMBINATION
Reverse of charge separation. In using this term it is important to
specify the resulting electronic state of the donor and acceptor.
CHARGE SEPARATION
A process in which, under the influence of a suitable driving force
(e.g. provided by photoexcitation), electronic charge moves in a direction
that increases the difference in local charges between donor and acceptor
sites. Electron transfer between neutral species is one of the most
important examples.
CHARGE SHIFT
A process in which under the influence of a suitable driving force
(e.g. provided by photoexcitation) electronic charge moves without
changing the difference in local charges between donor and acceptor
sites. Electron transfer reversing the charges in a system composed
of a neutral donor and a cationic acceptor or of a neutral acceptor
and an anionic donor provide prominent examples.
CHARGE-TRANSFER
(CT) STATE
A state related to the ground state by a charge transfer transition.
CHARGE-TRANSFER
(CT) TRANSITION
An electronic transition in which a large fraction of an electronic
charge is transferred from one region of a molecular entity, called
the electron donor, to another, called the electron acceptor (intramolecular
CT) or from one molecular entity to another (intermolecular CT). Typical
for donor-acceptor complexes or multichromophoric molecular entities.
In some cases the charge transfer absorption band may be obscured
by the absorption of the partners.
CHARGE-TRANSFER
(CT) COMPLEX
A ground-state complex which exhibits an observable charge transfer
absorption band.
See charge-transfer
(CT) transition.
CHARGE-TRANSFER
TRANSITION TO SOLVENT (CTTS)
Electronic transition which is adequately described by single electron
transfer between a solute and the solvent, as opposed to excitation
followed by electron transfer to solvent.
See also charge-transfer
(CT) transition
CHEMICAL LASER
A CW or pulsed laser in which the excitation and population inversion
of the emitting species results from a chemical reaction. Typical
examples are HF and DF lasers emitting many lines in the IR region.
CHEMIEXCITATION
Generation, by a chemical reaction, of electronically excited molecular
entities from reactants in their ground electronic states.
CHEMILUMINESCENCE
Luminescence arising from chemiexcitation.
CHROMOPHORE
That part of a molecular entity consisting of an atom or group of
atoms in which the electronic transition responsible for a given spectral
band is approximately localized.
CIDEP (Chemically Induced Dynamic
Electron Polarization)
Non-Boltzmann electron spin state population produced in thermal or
photochemical reactions, either from a combination of radical pairs
(called radical-pair mechanism), or directly from the triplet state
(called triplet mechanism), and detected by ESR spectroscopy.
CIDNP (Chemically Induced Dynamic
Nuclear Polarization)
Non-Boltzmann nuclear spin state distribution produced in thermal
or photochemical reactions, usually from a combination of radical
pairs, and detected by NMR spectroscopy.
CIEEL (Chemically Initiated Electron
Exchange Luminescence)
A type of luminescence resulting from a thermal electron-transfer
reaction.
Also called catalyzed chemiluminescence.
COLLISION COMPLEX
An ensemble formed by two reaction partners for which the distance
is the sum of their Van der Waals radii. As such it constitutes a
subclass of the species indicated as encounter complex.
See also encounter
complex.
CO2 LASER
A continuous or pulsed source of coherent radiation normally tunable
through the CO2 vibration-rotation band centered near 10.6
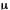 m.
m.
See gas lasers, laser.
COHERENT RADIATION
A source is said to emit coherent radiation when all the elementary
waves emitted have a phase difference constant in space and time.
CONDUCTION BAND
A vacant or only partially occupied set of many closely spaced electronic
levels resulting from an array of a large number of atoms forming
a system in which the electrons can move freely or nearly so. This
term is usually used to describe the properties of metals and semiconductors.
See bandgap energy,
Fermi level, valence
band.
CONFIGURATION (Electronic
Configuration)
A distribution of the electrons of an atom or a molecular entity over
a set of one-electron wavefunctions called orbitals, according to
the Pauli principle. From one configuration several states with different
multiplicities may result. For example, the ground electronic configuration
of the oxygen molecule (O2) is 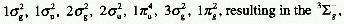
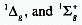 states of different energy.
states of different energy.
CONFIGURATION INTERACTION
(CI)
The mixing of wavefunctions representing different electronic configurations
to obtain an improved wavefunction for a many-electron state.
CONTACT ION PAIR
Pair of ions in direct contact and not separated by an intervening
solvent or other neutral molecule. One mode of formation for a (geminate)
contact ion pair is electron transfer between precursor species in
an encounter complex (cf. collision complex ). If one of the precursors
in the encounter complex is electronically excited the contact ion
pair formed by electron transfer is equivalent to a polar exciplex.
CONVERSION SPECTRUM
A plot of a quantity related to the absorption (absorbance, cross
section, etc.) multiplied by the quantum yield for the considered
process against a suitable measure of photon energy, such as frequency,
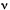 ,
wavenumber,
,
wavenumber, 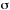 ,
or wavelength,
,
or wavelength, 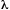 .
E.g., the conversion cross section,
.
E.g., the conversion cross section, 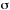
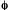 ,
has the SI unit m2.
,
has the SI unit m2.
See also action spectrum,
efficiency spectrum, spectral
effectiveness.
COPPER VAPOUR LASER
A pulsed source of coherent radiation emitting at 578.2 and 510.5
nm from excited copper atoms.
See gas lasers, laser.
CORRELATION DIAGRAM
A diagram which shows the relative energies of orbitals, configurations,
valence bond structures, or states of reactants and products of a
reaction, as a function of the molecular geometry, or another suitable
parameter. An example involves the interpolation between the energies
obtained for the united atoms and the values for the separated atoms
limits.
CORRELATION ENERGY
The difference between the Hartree-Fock energy calculated for a system
and the exact nonrelativistic energy of that system. The correlation
energy arises from the approximate representation of the electron-electron
repulsions in the Hartree-Fock method.
CRITICAL QUENCHING
RADIUS ( r0 )
See Förster excitation
transfer
CRYSTAL FIELD SPLITTING
The removal of a degeneracy of the energy levels of molecular entities
or ions due to the lower site symmetry created by a crystalline environment.
This term is sometimes incorrectly used synonymously with the term
ligand field splitting.
CT
Abbreviation for charge-transfer.
CURRENT YIELD
See photocurrent yield.
CUT-OFF FILTER
An optical device which only permits the transmission of radiation
of wavelengths that are longer than or shorter than a specified wavelength.
Usually, the term refers to devices which transmit radiation of wavelengths
longer than the specified wavelength.
See filter.
CW (Continuous Wave)
Nonpulsed source of electromagnetic radiation.
[A] [B] [C]
[D] [E] [F]
[G] [H] [I]
[J] [K] [L]
[M]
[N] [O] [P]
[Q] [R] [S]
[T] [U] [V]
[W] [X] [Y]
[Z]

