Glossary of Terms Used in Photochemistry
[A] [B] [C]
[D] [E] [F]
[G] [H] [I]
[J] [K] [L]
[M]
[N] [O] [P]
[Q] [R] [S]
[T] [U] [V] [W]
[X] [Y] [Z]
GAS LASERS
CW or pulsed lasers in which the active medium is a gaseous mixture
usually composed of a buffer gas (He for instance) and an active medium
consisting of:
- neutral atoms (e. g., Ne, Cu, Au, etc.) or molecules
(e.g., N2, CO2, CO, I2, etc.), or
- ionized atoms (e. g., Ar, Kr, Cd, etc.)
These lasers are not tunable but most of them can emit
several lines which in many cases may be selected from a single apparatus.
Pulsed lasers may be free-running, Q-switched, or mode-locked.
Some CW lasers may be mode-locked.
See argon ion laser,
CO2 laser, excimer
laser, copper vapour laser,
helium-neon laser, krypton
ion laser, nitrogen laser.
GAUSSIAN BAND SHAPE
A band shape described by the Gaussian function
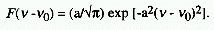 .
.
In this equation, a-1 is proportional to
the width of the band, and n0 is the frequency of the band
maximum.
See also Lorentzian
band shape.
GEMINATE ION PAIR
Ion pair, formed from a precursor that constitutes a single kinetic
entity. I.e. by electron transfer or ion transfer in an encounter
complex (cf. collision complex) or by ionic dissociation of a single
molecular entity.
GEMINATE PAIR
Pair of molecular (or atomic) species in close proximity in liquid
solution with a solvent cage and resulting from reaction (e.g. bond
scission, electron transfer, group transfer) of a precursor that constitutes
a single kinetic entity.
GEMINATE RECOMBINATION
Recombination reaction of a geminate pair. The reaction can either
be a back electron transfer that restores the donor and acceptor species
in their ground-state, from which the pair was created via electron
transfer, or a bond formation or bond reorganization.
GROUND STATE
The lowest energy state of a chemical entity. In photochemistry ground
electronic state is usually meant.

