Glossary of Terms Used in Photochemistry
[A] [B] [C]
[D] [E] [F]
[G] [H] [I]
[J] [K] [L]
[M]
[N] [O] [P]
[Q] [R] [S]
[T] [U] [V] [W]
[X] [Y] [Z]
FACTOR-GROUP SPLITTING
See Davydov splitting.
FERMI LEVEL (EF)
The chemical potential of electrons in a solid (metals, semiconductors
or insulators) or in an electrolyte solution.
See bandgap energy,
conduction band, valence
band.
FILTER (optical)
A device which reduces the spectral range (bandpass, cut-off, and
interference filter) or radiant power of incident radiation (neutral
density or attenuance filter) upon transmission of radiation.
FLASH PHOTOLYSIS
A technique of transient spectroscopy and transient kinetic studies
in which a light pulse is used to produce transient species. Commonly,
an intense pulse of short duration is used to produce a sufficient
concentration of a transient species suitable for spectroscopic observation.
FLUENCE (H0)
When applied to energy, it is the total radiant energy traversing
a small transparent imaginary spherical target containing the point
under consideration, divided by the cross section of this target.
The product of the fluence rate and the duration of the irradiation
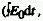 , simplified expression: H0
= E0 t when the fluence rate is constant over the time
considered). The SI unit is J m-2. Energy fluence is identical
to spherical radiant exposure and reduces to radiant exposure (H)
for a parallel and normally incident beam, not scattered or reflected
by the target or its surroundings.
, simplified expression: H0
= E0 t when the fluence rate is constant over the time
considered). The SI unit is J m-2. Energy fluence is identical
to spherical radiant exposure and reduces to radiant exposure (H)
for a parallel and normally incident beam, not scattered or reflected
by the target or its surroundings.
See also dose, photon
fluence.
FLUENCE RATE (E0)
The rate of fluence, H0. Four times the ratio of the radiant
power, P, incident on a small transparent imaginary spherical volume
element containing the point under consideration, divided by the surface
area of that sphere, SK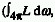 simplified expression: E0 = 4 P/SK when the
radiant power is constant over the solid angle considered). For energy
fluence rate the SI unit is Wm -2. It reduces to irradiance,
E, for a parallel and perpendicularly incident beam not scattered
or reflected by the target or its surroundings.
simplified expression: E0 = 4 P/SK when the
radiant power is constant over the solid angle considered). For energy
fluence rate the SI unit is Wm -2. It reduces to irradiance,
E, for a parallel and perpendicularly incident beam not scattered
or reflected by the target or its surroundings.
See intensity, radiance.
See also photon
fluence rate.
FLUORESCENCE
Spontaneous emission of radiation (luminescence) from an excited molecular
entity with the formation of a molecular entity of the same spin multiplicity
.
FLUX (energy flux)
See radiant energy flux, radiant
power.
f NUMBER
See oscillator strength.
FÖRSTER
EXCITATION TRANSFER (Dipole-Dipole Excitation Transfer)
A mechanism of excitation transfer which can occur between molecular
entities separated by distances considerably exceeding the sum of
their van der Waals radii. It is described in terms of an interaction
between the transition dipole moments, (a dipolar mechanism). The
transfer rate constant 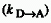 is
given by
is
given by
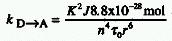
where K is an orientation factor, n the refractive
index of the medium,  0
the radiative lifetime of the donor, r the distance (cm) between donor
(D) and acceptor (A), and J the spectral overlap (in coherent units
cm6 mol-1) between the absorption spectrum of
the acceptor and the fluorescence spectrum of the donor. The critical
quenching radius, r0, is that distance at which
0
the radiative lifetime of the donor, r the distance (cm) between donor
(D) and acceptor (A), and J the spectral overlap (in coherent units
cm6 mol-1) between the absorption spectrum of
the acceptor and the fluorescence spectrum of the donor. The critical
quenching radius, r0, is that distance at which 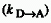 is equal to the inverse of the radiative lifetime.
is equal to the inverse of the radiative lifetime.
See also Dexter
excitation transfer, energy transfer,
radiative energy transfer.
FÖRSTER CYCLE
Indirect method of determination of excited state equilibria, such
as pK*,a values, based on ground state thermodynamics and
electronic transition energies. This cycle considers only the difference
in molar enthalpy change (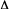
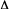 H
) of reaction of ground and excited states, neglecting the difference
in molar entropy change of reaction of those states (
H
) of reaction of ground and excited states, neglecting the difference
in molar entropy change of reaction of those states (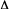
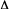 S).
S).
FOURIER TRANSFORM
SPECTROMETER
A scanning interferometer, containing no principal dispersive element,
which first splits a beam into two or more components, then recombines
these with a phase difference. The spectrum is obtained by a Fourier
transformation of the output of the interferometer.
FRANCK-CONDON PRINCIPLE
Classically, the Franck-Condon principle is the approximation that
an electronic transition is most likely to occur without changes in
the positions of the nuclei in the molecular entity and its environment.
The resulting state is called a Franck-Condon state, and the transition
involved, a vertical transition.
The quantum mechanical formulation of this principle is that the intensity
of a vibronic transition is proportional to the square of the overlap
integral between the vibrational wavefunctions of the two states that
are involved in the transition.
FRANCK-CONDON STATE
See Franck-Condon principle.
FREE ELECTRON LASER
Source of coherent radiation in which the active medium is an electron
beam moving at speeds close to the speed of light in the spatially
periodic magnetic field produced by an array of magnets (the wiggler).
The emitted wavelength, 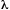 L,
is approximately given by
L,
is approximately given by 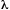
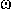 /(4E2
), with
/(4E2
), with 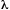
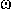 being the wiggler period and E the kinetic energy of the electrons
in MeV.
being the wiggler period and E the kinetic energy of the electrons
in MeV.
See laser.
FREE-RUNNING LASER
It applies to a pulsed laser and means that the laser emission lasts
as long as the pumping process is sufficient to sustain lasing conditions.
Typical pulse durations are in the 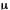 s-ms
range, depending on the pumping source. When the operation mode of
a pulsed laser is not specified as Q-switched, mode-locked, or anything
else, it must be considered as free-running.
s-ms
range, depending on the pumping source. When the operation mode of
a pulsed laser is not specified as Q-switched, mode-locked, or anything
else, it must be considered as free-running.
FREQUENCY (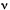 or
or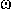 )
)
The number of waveperiods per unit time. The linear frequency, n,
is the number of cycles per unit time. The SI unit is
Hz  s-1. For the angular frequency, the symbol
s-1. For the angular frequency, the symbol 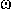 (= 2
(= 2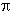
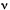 )
is used, with rad s-1 as the SI unit.
)
is used, with rad s-1 as the SI unit.
FREQUENCY DOUBLING
See harmonic frequency
generation, nonlinear
optical effects.
FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum)
See half-(band)width.

