BP04 Threading together amino acids via peptide links
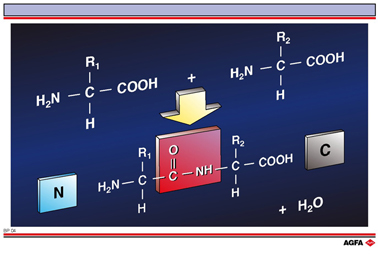
Aim: To show that peptides can be built from amino acid building blocks via the formation of peptide links. |
Amino acids can be covalently linked to each other by the formation of an amide bond between the alphaamino group of the first amino acid and the alpha-carboxyl group of the second amino acid.
When noting
down the primary structure that is formed by the peptide bond we use the three letter
codes of the amino acids involved.
The oligopeptide
N Gly-Leu-Ser-Asp C
indicates the combination of glycine, leucine, serine, and aspartic acid. By convention, the N-terminus is on the left and the C-terminus on the right.