L04 Desulphurisation of smoke
Aim: To show how sulphur is removed from smoke |
Ideally, fuel should be
made sulphur-free before burning, as occurs with some of the gas from the gas fields in
the Netherlands. If this is not possible, the sulphur can be removed from the exhaust
gases of large furnaces in a number of ways. The wet desulphurisation process is shown in
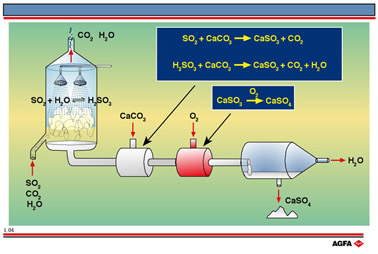
a simplified form on illustration L4.
The sulphur-containing exhaust gas is passed through a reaction chamber. Water is sprayed
into the top of the chamber and the water droplets as they fall absorb sulphur dioxide :
![]()
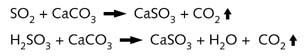
This calcium sulphite is further oxidised with oxygen from the air in an oxidation reactor
to calcium sulphate.
![]()
The product can be used in the manufacture of plaster, but the quantities are such that
most of it is dumped.