ST10
Separation of a heterogeneous solid - liquid mixture
| Aim:
To introduce the idea of centrifuging as a separation technique
for heterogeneous solid - liquid and liquid – liquid mixtures. |
In a centrifuge, a fast circular movement around a fixed axis exerts an outward-working force on the particles that are to be separated. This force is proportional to the speed of rotation, the distance from the axis and the mass of the particles. In this way heavier particles can be separated from lighter ones. These heavier particles move furthest away from the axis during the centrifuging process. After centrifuging the heaviest particles are thus to be found at the bottom of the tube. This process is used if precipitation is too slow or impossible because the force of gravity is insufficient. Since the forces generated by the centrifuge are much greater than those of gravity, separation becomes both possible and fast.
An
application of this technique that is currently attracting media attention
is in investigation of blood-doping on top sportsmen. Blood-doping means
that by using illegal substances the number of red blood cells, responsible
for transport of oxygen, is artificially increased. This improves the
sportsman’s performance.
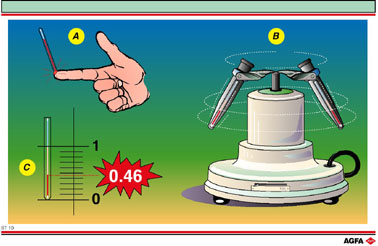
The number of red blood cells can be estimated by determining the hematocrite.
The hematocrite is the volume fraction of the red blood cells (erythrocytes)
as a function of the total blood volume. A blood sample is obtained by
a prick in the finger, and the blood is sucked up into a thin glass capillary
tube (A) by capillary force. This capillary tube is then sealed off with
wax at the top and bottom and placed in a centrifuge (B). The tube is
centrifuged for a few minutes. The heavier red blood cells gather at the
bottom of the capillary. After centrifuging the height of the column of
red blood cells is compared to the total liquid level in the capillary
(the sum of the height of the red blood cells and the layer of serum above
them) by reading off a calibrated scale (C). In a normal blood sample
the hematocrite is assumed to have a maximum value of 0.50. Values above
0.50 indicate blood doping and the top sportsmen can expect sanctions.
Centrifuging not only speeds up the precipitation of solid particles but
also makes it possible to separate liquid from solid particles directly.
In this case a porous or perforated wall is introduced onto the vessel.
This wall ensures that the heavier particles are held back whilst the
liquid is centrifuged away. Well-known examples are a salad dryer or a
spin dryer for removing excess water from washing.