| Area of surface42 |
| 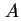 , ,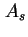 , ,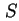 |
| Specific surface area (= surface area per unit mass)43 |
| 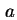 , ,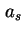 , ,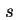 |
| Thickness of surface layer |
| 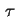 |
| Superscript, indicating quantities referring to the surface layer or interfacial layer |
| 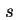 |
| Volume of interfacial layer |
| 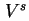 |
| Subscript, indicating quantities relating to monolayer capacity |
| 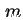 |
| Surface coverage (= amount of adsorbed substance divided by monolayer capacity) |
| 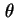 |
Area per molecule in complete monolayer of substance 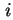 |
| 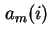 |
| Superscript, indicating excess quantities referring to the Gibbs surface |
| 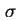 |
Surface excess amount, Gibbs adsorption of component 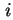 ( (
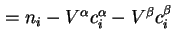 ) ) |
|
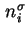 |
Total surface excess amount (of adsorbed substance)
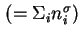 |
|
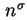 |
Gibbs surface concentration, surface excess concentration
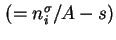 |
|
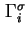 |
Total Gibbs surface concentration, total surface excess concentration
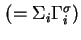 |
|
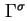 |
Surface excess number of molecules (of component 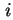 ) ) |
|
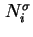 |
Surface excess mass (of component 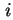 ) ) |
|
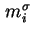 |
Relative adsorption of component 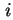 with respect to component 1 with respect to component 1
|
|
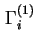 , ,
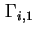 |
Reduced adsorption (of component 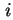 ) )
|
|
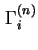 |
Total concentration in phase 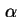
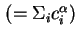 |
|
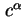 |
Area per molecule in surface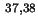 |
| 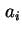 , ,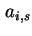 |
Co-area per molecule in surface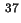 |
| 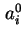 , ,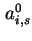 |
Gibbs surface concentration (for solid/liquid systems) of component 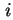 , relative to a reference system with the same number of moles (reduced adsorption) , relative to a reference system with the same number of moles (reduced adsorption) |
|
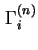 |
(
![$ =A_s^{-1}\left[n_i-n^lx_i^l\right]$](img490.png) ) ) |
| |
| Relative adsorption (for solid/liquid systems) |
|
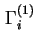 |
(
![$ =A_s^{-1}\left[n_i-n^lx_i^l/x_1^l\right]={\Gamma}_i^{(n)}/x_1^l$](img491.png) for binary system) for binary system) |
| |
Gibbs surface concentration (for solid/liquid systems) of component 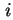 , relative to a reference system with the same volume of liquid
( , relative to a reference system with the same volume of liquid
(
![$ =A_s^{-1}\left[n_i-c_i^lV^l\right]$](img492.png) ) ) |
|
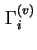 |
| Surface excess volume of gas calculated for 273.15 K and 101.325 kPa (0 and 1 atm) |
|
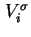 |
Amount of adsorbed component 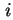 (= amount of component (= amount of component 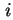 in the interfacial layer) in the interfacial layer) |
| 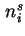 |
Total amount of adsorbed substance
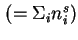 |
| 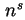 |
| Monolayer capacity expressed as amount of substance |
| 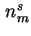 |
| Monolayer capacity expressed in volume of gas calculated for 273.15 K and 101.325 kPa |
| 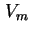 |
![$\displaystyle \left[={\Gamma}_i^{\sigma}-{\Gamma}_1^{\sigma}\left(\frac{c_i^{\alpha}-c_i^{\beta}}{c_1^{\alpha}-c_1^{\beta}}\right)\right]$](img483.png)
![$\displaystyle \left[={\Gamma}_i^{\sigma}-{\Gamma}^{\sigma}\left(\frac{c_i^{\alpha}-c_i^{\beta}}{c^{\alpha}-c^{\beta}}\right)\right]$](img484.png)
![$ =A_s^{-1}\left[n_i-n^lx_i^l/x_1^l\right]={\Gamma}_i^{(n)}/x_1^l$](img491.png) for binary system)
for binary system)![$\displaystyle \left[={\Gamma}_i^{\sigma}-{\Gamma}_1^{\sigma}\left(\frac{c_i^{\alpha}-c_i^{\beta}}{c_1^{\alpha}-c_1^{\beta}}\right)\right]$](img483.png)
![$\displaystyle \left[={\Gamma}_i^{\sigma}-{\Gamma}^{\sigma}\left(\frac{c_i^{\alpha}-c_i^{\beta}}{c^{\alpha}-c^{\beta}}\right)\right]$](img484.png)
![$ =A_s^{-1}\left[n_i-n^lx_i^l/x_1^l\right]={\Gamma}_i^{(n)}/x_1^l$](img491.png) for binary system)
for binary system)