|
|
Vol.
27 No. 2
March-April 2005
Special Topic Articles Featuring the 2004 Winners of the IUPAC Prize for Young Chemists
Pure and Applied Chemistry
Vol. 76, No. 12, pp. 2051–2099, 2004
The IUPAC Prize for Young Chemists encourages young scientists throughout the world to enter an annual competition that requires candidates to submit short essays based upon the topic of their Ph.D. studies. Starting in 2002, prizewinners have been invited to submit manuscripts on aspects of their research topics for consideration as short, critical review articles to be published in Pure and Applied Chemistry. Following peer review, the first collection appeared in PAC 74(11), 2021–2081 (2002) and encouraged the view that it offers sufficient readership appeal to become a regular special topic feature of the journal. The second series, covering the works of the 2003 winners was published in PAC 76(2), 263–319 (2004). The most recent series of articles was published in the Dec 2004 issue of PAC and includes the following critical reviews:
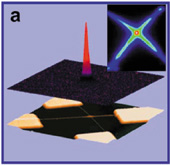 |
Crossed InP nanowire LED. (top) Three-dimensional (3D) plot of light intensity of the electroluminescence from a crossed NW LED. Light is only observed around the crossing region. (bottom) 3D atomic force microscope image of a crossed NW LED. (inset) Photolumine-scence image of a crossed NW junction. Y. Huan and C.M. Lieber, PAC 76(12), 2051-2068 (2004). |
“Integrated
Nanoscale Electronics and Optoelectronics: Exploring Nanoscale
Science and Technology through Semiconductor Nanowires,”
by Y. Huan
Semiconductor
nanowires (NWs) represent an ideal system for investigating
low-dimensional physics and are expected to play an important
role as both interconnects and functional device elements
in nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic devices. In their
review, Huang and Lieber look at a series of key advances
defining a new paradigm of bottom-up assembling integrated
nanosystems using semiconductor NW building blocks. They first
introduce a general approach for the synthesis of a broad
range of semiconductor NWs with precisely controlled chemical
composition, physical dimension, and electronic, optical properties
using a metal cluster catalyzed vapor-liquid-solid growth
mechanism. Subsequently, they describe rational strategies
for the hierarchical assembly of NW building blocks into functional
devices and complex architectures based on electric field
or micro-fluidic flow. Next, they discuss a variety of new
nanoscale electronic device concepts including crossed NW
p-n diode and crossed NW field effect transistors (FETs).
Lastly, they describe a wide range of photonic and optoelectronic
devices, including nanoscale light-emitting diode (nanoLED),
multicolor LED arrays, integrated nanoLED-nanoFET array, single
nanowire waveguide, and single nanowire nanolaser. The potential
application of these nanoscale light sources for chemical
and biological analyses is also discussed.
 |
|
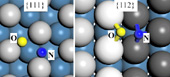
Typical
transition state structures of NO dissociation on the
close-packed {111} surface and the stepped {211} surface.
Z.-P. Liu, PAC 76(12), 2069-2083 (2004).
|
“Chemical
Reactions at Surfaces and Interfaces from First Principles:
Theory and Application,” by Z.-P. Liu
The last decade has seen rapid expansion and development in
the field of density functional theory (DFT) simulation on
the complex chemical processes that occur at surfaces and
interfaces. The understanding of the phenomena in surface
science and heterogeneous catalysis has benefited tremendously
from these quantum mechanic calculations. Liu reviews the
current progress in the theory of reactions on surfaces, in
particular those relevant to the barrier and the active site
of surface reactions. Two representative reactions, namely
NO dissociation and CO oxidation, are selected to illustrate
how these theoretical concepts are applied to understand catalytic
reactions. Here, the pathways and the energetics of these
reactions under various catalytic conditions are described
in detail and the understanding of the reactions is generalized.
It is concluded that DFT-based methods can be well applied
to catalysis to understand the electronic structure of chemical
processes and to elucidate mechanisms of complex surface reactions.
“Modeling Prebiotic Catalysis with Nucleic Acid-Like Polymers and its Implications for the Proposed RNA World,” by S.G. Srivatsan
The theory that RNA molecules played a pivotal role in the early evolution of life is now widely accepted. Studies related to this hypothetical “RNA world” include three major areas: the formation of precursors for the first RNA molecules, the polymerization process, and the potential of RNA to catalyze chemical and biochemical reactions. Several chemical and biochemical studies performed under simulated prebiotic conditions support the role of RNA as both genetic as well as catalytic material. However, due to the lack of credible mechanism for de novo nucleic acid synthesis and the hydrolytic instability of RNA molecules, there has been some serious discussion of whether biopolymers that closely resembled nucleic acid preceded the “RNA world.” In this context, an overview of prebiotic chemistry, the role of the mineral surface, and the significance of studies related to RNA-like polymers in the origin of life are presented in Srivatsan’s review.
|
Probable events related to the origin of life. S.G. Srivatsan, PAC 76(12), 2085-2099 (2004). |
www.iupac.org/publications/pac/2004/7612
Page
last modified 1 March 2005.
Copyright © 2003-2005 International Union of Pure and
Applied Chemistry.
Questions regarding the website, please contact [email protected]
|