Glossary of Terms Used in Combinatorial
Chemistry
[A-B]
[C] [D] [E-G]
[H-K] [L]
[M-N] [O-P] [Q] [R]
[S] [T] [U-Z]
R
Radiofrequency Encoding:
Strategy for identifying library members by physically associating them
with a set of electronic devices which emit characteristic radiofrequency
signals upon stimulation with a radiofrequency energy source. These
signals can be used to track the reaction history of each sample in
a synthesis 21,84.
Random Library: see Unbiased
Library
Ratio Coding: Encoding
strategy in which the relative quantities of tags
conveys information about compound identity. In comparison to binary
coding, more information may be obtained from a given tag set,
but tag interpretation is more complex 2,85.
Reagent Efficiency: The ratio
of the number of library members prepared compared to the number which
would have been prepared in a fully
combinatorial library using the same building
blocks. Lower reagent efficiency may be desirable in order to
reduce the number of compounds to be synthesized or tested, for example
by maximizing the number of members expected to have high activity in
a library prepared by parallel
synthesis 86.
Reagent Partitioning: Phenomenon
whereby the concentration of a compound within for instance a particle
of solid support is higher or lower than that of the bulk solution due
to the physicochemical properties of the solid support 87.
Recursive Partitioning:
Process for identifying complex structure-activity relationships in
large sets by dividing compounds into a hierarchy of smaller and more
homogeneous sub-groups on the basis of the statistically most significant
descriptors. See also clustering
and principal components
analysis 88,89.
Re-synthesis: Preparation of individual
members or pools
of a combinatorial library,
normally to follow up on some property of interest identified in initial
screening, and often in larger scale and/or greater purity than the
original preparation.
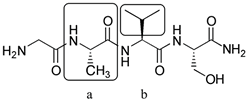
Residue: (a) Portion of a chemical structure
which can be identified as being derived from a particular building
block, such as the alanine residue in the peptide below; (b)
portion of a building block which is incorporated into the final product
but is not part of the scaffold,
such as the valine side-chain below.
Resin: Insoluble polymeric material which
allows ready separation from liquid-phase materials by filtration; can
be used to carry library members (i.e. solid
support) or reagents, or to trap excess reagents or reaction
by-products (see scavenger resin) 18.
Resin Capacity: see Capacity
Resin Loading: see Loading
Re-synthesis: Preparation of individual members or pools
of a combinatorial library,
normally to follow up on some property of interest identified in initial
screening, and often in larger scale and/or greater purity than the
original preparation.
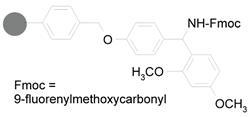
Rink Resin: Amide-releasing, acid-cleavable
solid support. 4-(2’,4’-Dimethoxyphenylaminomethyl)phenoxy
polystyrene 90.
Robotic System: Automated device
where materials are transfered by the physical movement of a delivery
device relative to the ultimate receptacle, or vice versa. See also
fluidic system 42.
Rules of Five: Lipinski’s
rules. Set of criteria for predicting the oral bioavailability
of a compound on the basis of simple molecular features (molecular weight,
c LogP, numbers of hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors).
Often used to profile a library or virtual
library with respect
to the proportion of drug-like members which it contains 91.

