L19 BOD and COD values
Aim: To show what these terms mean and how the values are measured. |
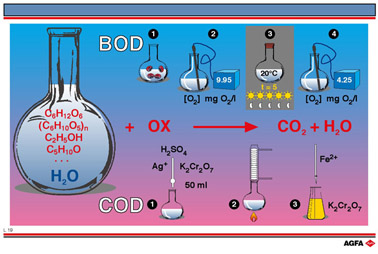
The BOD (biological
oxygen demand) value is the amount of oxygen required, with the assistance of bacteria, to
oxidise the oxidisable organic materials present in 1litre of water to carbon dioxide and
water. This is therefore a measure of the degree of pollution of the water and is
expressed in mg of oxygen /L.
To perform the test a small amount of bacteria is added to a measured quantity of dirty
water. The initial oxygen content is measured and then the water is kept in the dark for 5
days at a temperature of 20°C. No photosynthesis can occur under these conditions, so no
oxygen is produced. The oxygen content is then re-measured and the decrease in oxygen
content is called the BOD value.
A major disadvantage with this method is the time involved, the result only being available after 5 days. Another disadvantage is that toxic substances present in the water can adversely affect the bacteria making the measured BOD value too low.
If the BOD value is less than the
solubility of oxygen in water (1,38.10-3 mol/L; 44 mg/L), then the bacteria can
oxidise the polluting organic materials present in the water. If the BOD value is higher
than the solubility of oxygen then this cannot occur and the water remains polluted.
The COD value (chemical oxygen demand) indicates how much oxygen,
measured in mg/L is required to oxidise most of the organic material including cellulose
in 1litre of dirty water.
To perform this test a measured volume of acidified potassium dichromate solution is added
to the dirty water and the mixture is refluxed for 2hours at a temperature of 148°C.The
solution is then cooled and the quantity of remaining potassium dichromate is determined
by back titration using a solution of Fe2+ ions. From the amount of dichromate
that has been consumed the equivalent amount of oxygen in mg/L can be calculated.
This test method oxidises more organic material than the BOD test and therefore the COD
value is always higher than the BOD value. Despite this, measurement of the COD value is
often preferred because the results can be obtained more quickly.